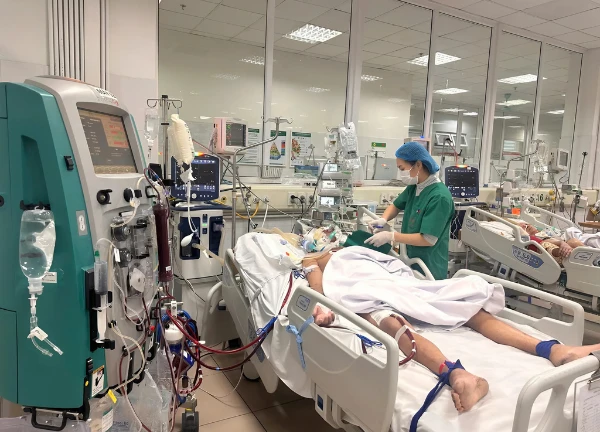
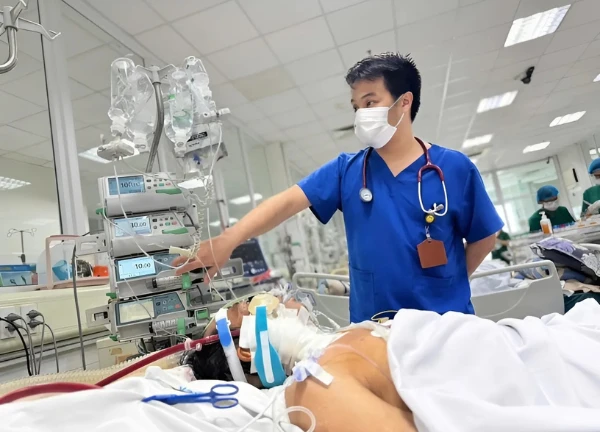
"Red alert": Seasonal flu breaks out strongly, Hanoi people "live in fear"?
4 | 0 Discuss | Share
Few people have saved more lives than Louis Pasteur. The vaccines he developed have protected billions of people around the world. Louis Pasteur's research on germs is considered to have revolutionized medicine. According to the BBC, Pasteur has completely changed humanity's understanding of biology, becoming the "father of microbiology".
Louis Pasteur was born on December 27, 1822 in Dole, in the Jura region of France. He was the fifth child in a family with generations of tanners. As a child, he was just an average student, diligent and passionate about painting. However, even as a young boy, he painted his family with a series of lifelike portraits, showing a keen observer eye, a man of great interest in precision and detail.
While teachers tried to support Pasteur to pursue art, his father wanted his son to focus on his studies. However, it was not until the last years of high school, encouraged by his teachers, that Pasteur began to undertake serious studies to make up for his academic shortcomings in order to enter the École Normale Supérieure - famous university in Paris. In 1840, he earned a bachelor of arts, and in 1842 a bachelor of science before earning a master's degree and then a doctorate in 1847.
Pasteur began his career in chemistry when he joined the University of Strasbourg. At the age of 25, he gave science his most important contribution when he demonstrated that identical molecules can exist as mirror images. This discovery of his is considered a fundamental step forward in microbiology, promoting the development of modern drugs and human understanding of DNA later.
During the 2,000 years from the time of Aristotle to the mid-19th century, people believed that life appeared spontaneously. For example, fleas are born from dust, while small creatures like maggots and bugs come from dead bodies. This comes from the fact that it is found that in stagnant ponds or on rotting animal carcasses there are no living things at first, but then maggots and bugs are swarming.
It was Pasteur who proved that those thoughts were completely wrong. By experimenting with a piece of meat, Pasteur proved that microorganisms and bacteria in the air are the cause of solutions such as sugar water, milk, broth... to be damaged and to preserve solutions. The fluid needs to be disinfected.
By the results of the study, he also concluded that these bacteria can also cause disease. At that time, his theory was controversial because Pasteur was a chemist, not a doctor. However, it was this same discovery that led to the development of disinfectants, which in turn changed the world of medicine forever.
In the early 19th century, in many European hospitals, maternal mortality was up to one-third due to infections in the hospital. In 1844, doctor Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis proved that postpartum fever was caused by an infection that was caused by doctors not washing their hands.
According to Semmelweis, it was the fact that doctors went straight from the autopsy room of people who had died of postpartum fever to the delivery room that transmitted the bacteria to the new patient and suggested washing hands before examining the mother but did not is approved.
In the US, Dr. Oliver Wendell Holmes also made a similar suggestion but was also criticized by medical experts. It was not until Louis Pasteur confirmed the existence of germs and established important principles of aseptic that "hand washing" became mandatory to prevent the spread of disease. Postoperative and postpartum mortality rates have since dropped dramatically.
After Pasteur made a splash with his germ theory, he was commissioned by King Napoleon III to deal with a problem facing the French wine industry at the time, which was that wine very often deteriorated during transportation. transfer.
After a series of careful experiments, Pasteur found that heating the wine to 55oC killed the bacteria without damaging the flavor. This process, later known as pasteurization, saved the French wine industry and spread Pasteur's reputation further. The sterilization process is still used today to protect food from spoilage.
After wine, Pasteur continued to save the French silk industry by discovering that silkworms were sick due to parasites and recommending measures to isolate and remove disease-carrying individuals.
In 1849, Louis Pasteur married Marie Laurent - daughter of the Rector of the University of Strasbourg where he held the position of Professor of Chemistry. The couple had 5 children together, but only 2 survived. In 1859, he lost a daughter to typhoid - a disease caused by drinking water and dirty food. In 1865, he lost a second daughter to the same disease. His third daughter also died in 1866 of a tumor. These great losses caused Pasteur to have a stroke, paralyzed the left side of his body at the age of 45.
However, that did not stop him from doing his research. On the contrary, in the face of personal loss, he plunged into work with greater intensity. Living at a time when young children often die from infectious diseases, he researched in hopes of stopping the situation.
After he suffered a stroke, his colleagues set up a mobile laboratory for him so he could work from his hospital bed. First, Pasteur and his team embarked on research on chicken cholera by injecting cholera bacteria into chickens. Through observation, with animals getting sick but not dying as usual, he realized that weak pathogens could help animals strengthen their immunity.
Next, he performed experiments with smallpox. A century earlier, Edward Jenner had discovered that smallpox could help fight smallpox. With his new discovery, Pasteur found a way to create a vaccine in the laboratory, leading to a turning point in the fight against infectious diseases.
Later, Pasteur came up with the idea of making vaccines for other diseases. After working on an anthrax vaccine, he continued with rabies. The first human rabies vaccine trial was successful on July 6, 1885, despite many reactions that Pasteur violated professional ethics because he did not have a license to practice medicine.
After presenting the results of his research on rabies to the French Academy of Sciences on March 1, 1886, Pasteur proposed the establishment of a rabies vaccine production facility and promptly received 2 million French francs in money. donations. In 1888, President Sadi Carnot built the first Pasteur Institute in France and then expanded to the colonial areas of this country such as Senegal, Ivory Coast.
Influenza A hits the world: 'Quadruple epidemic' raging, 'doomsday' imminent?  Khang Trần1 month agoThe influenza A epidemic is raging globally, putting great pressure on the health system and increasing hospitalizations. This year's flu season is more dangerous, with many countries facing overcrowding. Vaccinations and precautions are very important.
Khang Trần1 month agoThe influenza A epidemic is raging globally, putting great pressure on the health system and increasing hospitalizations. This year's flu season is more dangerous, with many countries facing overcrowding. Vaccinations and precautions are very important.

4 | 0 Discuss | Share
3 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share
2 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share
3 | 0 Discuss | Share

1 | 0 Discuss | Share

2 | 0 Discuss | Share

4 | 0 Discuss | Share

4 | 1 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share









2 | 0 Discuss | Report