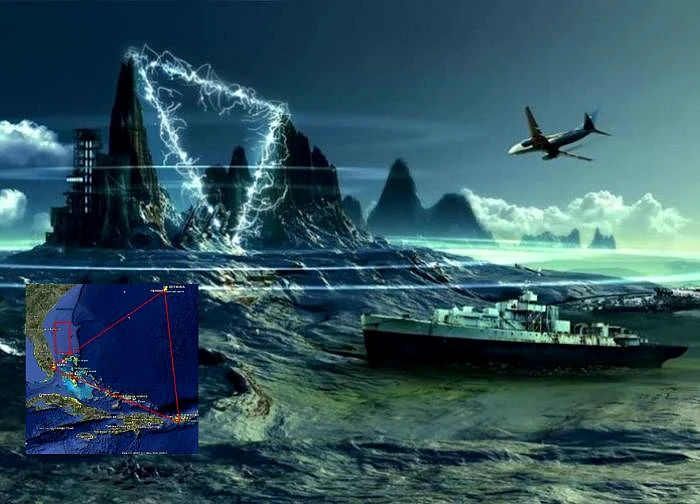
What is hidden at the bottom of the "devil's triangle" that makes planes and ships disappear?

2 | 0 Discuss | Share
After 2 years of absence, world-famous diva Celine Dion reappeared at the opening ceremony of the 2024 Paris Olympics. This is the first official performance of the female artist after many years of hiatus from singing due to a rare disease. " Stiff Person Syndrome " (SPS).
In December 2022, Celine Dion choked up to announce her poor health condition and announced a temporary suspension of artistic activities. The female singer tried to hold back tears when she said she had stiff person syndrome (SPS) - a very rare autoimmune-related movement disorder that affects the central nervous system (brain or spinal cord). This is a disease that affects only 1/1,000,000 people and there is still no cure.
According to the owner of the hit My Heart Will Go On, the stiff body disease causes the diva to lose muscle control, causing spasms. This affects Celine Dion's mobility.
"Stiff person syndrome" is a very rare autoimmune neurological disorder, with an incidence of only 1-2 people per 1 million people. The disease usually occurs between the ages of 30 and 60 and is more common in women, the incidence in women is twice as high as in men.
The disease causes muscle spasms and stiffness by affecting the brain and spinal cord's control of muscle activities. The disease often progresses gradually over time and can eventually cause disability, significantly reducing the patient's quality of life without appropriate treatment.
How does SPS disease manifest?
Most of the symptoms of the disease are caused by muscle spasticity. The disease progresses silently, intermittently, and can last from several months to several years, including:
- Numbness of limbs (legs, arms)
- Stiffness of the muscles in the trunk, abdominal muscles and back muscles.
- Changes in body shape due to stiffness of the muscles in the back can cause hunchback or lumbar lordosis.
- Difficulty walking or changing positions such as turning or bending.
Along with muscle stiffness comes painful muscle spasms. Muscle contractions can appear suddenly or when there are stimuli such as sudden movements, after strong noises or when touching the body. Patients may have symptoms such as jerking their legs or being startled. Sometimes the spasms are very strong and can cause falling while standing, or even breaking bones. Contractions occur automatically, can last several minutes or even hours, and require intravenous muscle relaxants to relieve them.
In addition, the disease also causes psychological disorders for patients. Anxiety disorders or depression, phobias can be caused by symptoms of the disease or by a deficiency of neurotransmitters in the brain. Feelings of anxiety and depression may increase when the patient goes out to public places.
In the later stages of the disease, the patient experiences more spasticity of the muscles and it can affect other parts of the body such as: causing spasticity of the facial muscles, reducing facial expressions. , spasticity of muscle groups related to breathing can be life-threatening.
Over time, the patient becomes more and more difficult to walk. Risk of falling, injury, or permanent disability and possibly needing a wheelchair in the later stages of the disease. The disease progresses in waves and can spread to other parts of the body. Currently, there is no specific treatment for the disease, symptomatic treatments only help alleviate and improve the patient's quality of life.
What is the cause of the disease?
In people with autoimmune disorders, the body's immune system mistakenly identifies the body's healthy cells and tissues as pathogens and attacks them. About 80% of patients have GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase) antibodies. This antibody attacks proteins in nerve cells that control muscle activity, affecting the spinal cord and brain function.
The cause of this autoimmune disorder is unknown, although genetics may play a role.
SPS disease may be more common in people with other accompanying autoimmune diseases such as pernicious anemia, vitiligo, diabetes, autoimmune thyroiditis, Celiac disease (an allergy to proteins that contain in wheat).
In addition, researchers also found a link between the rare paracancerous form of SPS and various cancers including: breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, thyroid cancer, Hodgkin's or non-Hodgkin's disease.
To diagnose the disease, experts will ask about the patient's history and medical history to rule out other diseases that also cause muscle spasms such as MS, Parkinson's disease..., and at the same time, Necessary tests include:
- Blood test for GAD antibodies: 80% of patients have this antibody in their blood.
- Electromyography: This method measures and evaluates electrical activity in muscles.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain and spinal cord to rule out other causes that cause similar symptoms and check for other autoimmune conditions.
How to treat this disease?
Currently, there is no thorough treatment for SPS. Symptomatic treatments help slow the progression of the disease and improve the patient's quality of life. One or more of the following drug groups may be used:
- Muscle relaxants
- Neuroleptics such as benzodiazepines (diazepam...)
- Antiepileptic drugs such as Neurontin
- Anticonvulsants
- Analgesic
- Antidepressants
Combined with drugs that change the disease's immunity: plasmapheresis... or combined with physical therapy, massage...

2 | 0 Discuss | Share

1 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share
4 | 0 Discuss | Share
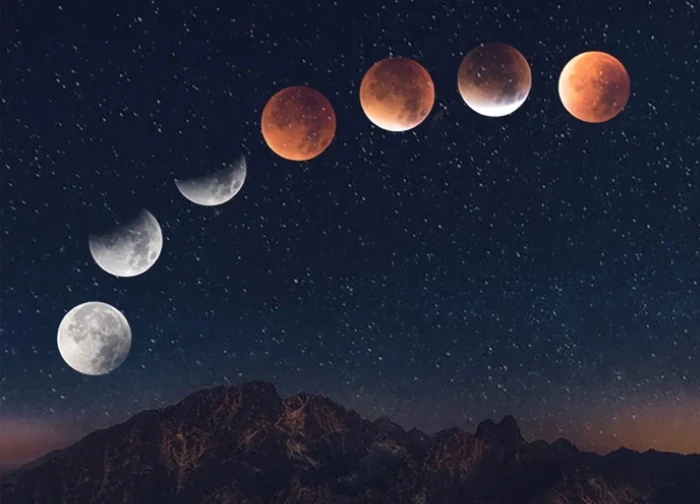

4 | 0 Discuss | Share

3 | 0 Discuss | Share
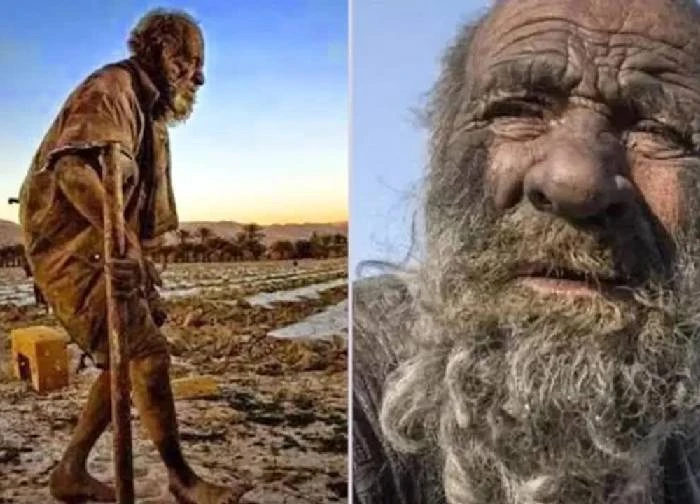

0 | 0 Discuss | Share

0 | 0 Discuss | Share
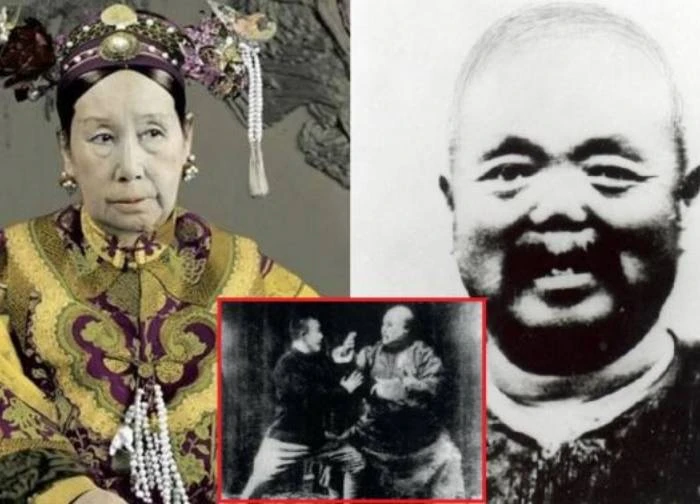

1 | 0 Discuss | Share
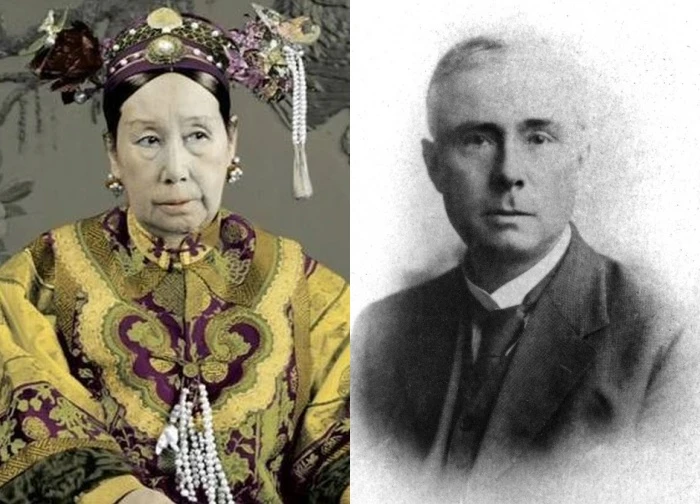

4 | 0 Discuss | Share



1 | 1 Discuss | Report